Understanding the Benefits of Professional Roof Coating Services
Why Roof Coatings Matter: Introduction and Outline
Your roof is more than a lid on the building; it is the quiet partner that shields structure, finishes, and people from the slow, persistent forces of time. Professional coating services help that partner last longer and perform more reliably by targeting three fundamentals: keeping water out, controlling heat flow, and managing sunlight. In practice, that means a well-prepared surface, a compatible waterproofing or protective layer, and a plan for upkeep. When those elements align, coatings can extend service life, stabilize interior comfort, and defer costly tear-offs—without flashy promises or shortcuts.
To keep this journey clear and useful, here is the road map we will follow, with practical points woven into each stop:
– Waterproofing: how liquid-applied membranes and reinforced systems block leaks, what substrates demand, and why details decide outcomes.
– Insulation: the role of R-value per inch, thermal bridges, and air control in keeping heat where you want it.
– Reflective coatings: how solar reflectance and thermal emittance curb rooftop temperatures and lower cooling demand.
– Costs and maintenance: budgets, life-cycle payback, inspection routines, and recoat timing.
– Professional process: assessment, preparation, application, and quality assurance you can ask for and verify.
Why now? Weather extremes, higher energy rates, and sustainability goals have made roof performance inseparable from business continuity and household comfort. A small split at a seam or a wet patch of insulation can ripple into damaged interiors and rising utility bills, but thoughtful upgrades turn the roof into a steadying force. Expect measured gains rather than magic: leak risk drops when moisture pathways are sealed; cooling loads fall when sunlight is reflected; heating steadies when insulation continuity improves. Results vary with climate, occupancy, and building type, yet the underlying physics are consistent: control water, control heat, control sun, and the whole building benefits.
Waterproofing: Systems, Substrates, and Moisture Control
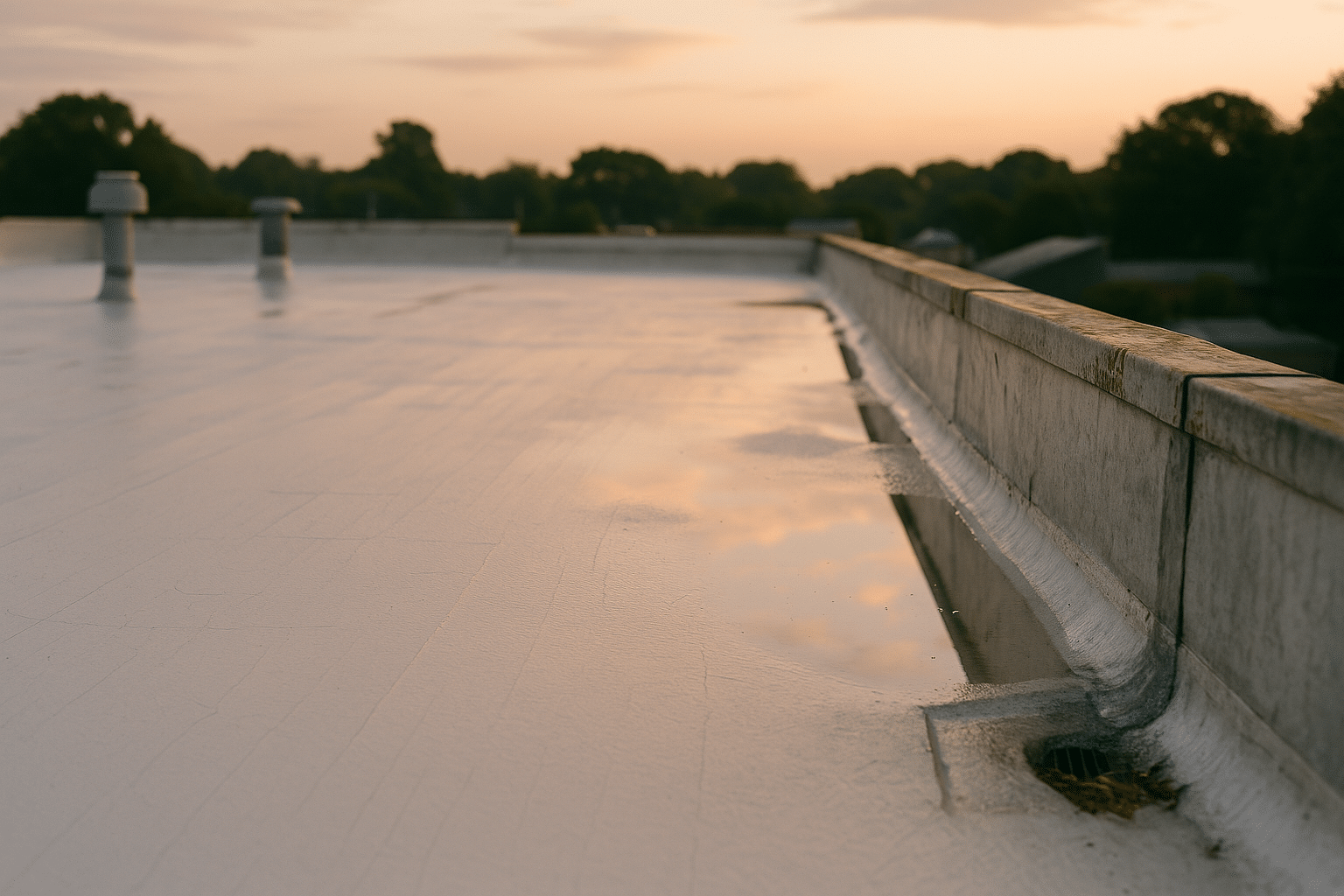
Water finds the smallest invitation—hairline cracks at parapets, unsealed fasteners, aging flashings—so effective waterproofing begins with surface diagnosis. Moisture scans, core cuts, and a close look at terminations reveal whether a coating-only approach is suitable or whether localized repairs are needed first. Professional crews prioritize preparation because adhesion determines success; a clean, dry, and sound substrate is nonnegotiable. Typical steps include pressure washing, rust conversion on metal, patching blisters, priming chalky surfaces, and rebuilding failing details with reinforcing fabric.
Liquid-applied membranes create continuous barriers over varied roof types, including metal, single-ply, and modified bitumen. Options range from elastomeric acrylics to polyurethanes and silicones, each with different strengths. Broadly speaking, elongation in the 150–400% range lets a membrane move with thermal expansion and contraction; tensile strength in the low hundreds of psi helps it resist mechanical stress. Thickness matters: a dry film build of roughly 20–40 mils for coatings or 60–90 mils for heavier liquid membranes is common, applied in multiple passes for consistency. Seams, penetrations, and transitions receive fabric reinforcement to distribute stress and seal micro-gaps that cause capillary leaks.
Moisture control is as much about drying potential as it is about blocking water. On some roofs, a vapor-permeable topcoat helps trapped moisture escape; on others, especially where interior humidity is high, a tighter membrane reduces vapor drive into insulation. The right choice depends on climate and usage. For instance, in cold regions, uncontrolled vapor can condense within the assembly during winter, leading to insulation degradation; in warm, humid climates, inward vapor drive on cool, air-conditioned roofs can cause persistent dampness beneath the surface. Drainage shapes outcomes too. Even quality membranes fatigue under standing water, so improving slope at ponding zones, clearing scuppers, and maintaining drains are crucial to long-term performance.
It is tempting to focus on square footage coverage rates, but details govern durability. Professionals document adhesion pull-off values, check wet and dry film thickness during application, and stage work around weather windows to avoid wash-off or dew interference. They also return after the first significant rain to inspect terminations and repairs. The result is a roof that sheds water predictably, turning storm noise into nothing more than a gentle drumbeat overhead.
Insulation: R-Value, Airtightness, and Real-World Comfort
Insulation does more than add R-value to a specification; it stabilizes interior temperatures, slows heat loss in winter, and limits heat gain in summer. Common roof insulations include polyisocyanurate, expanded polystyrene, extruded polystyrene, mineral wool, and closed-cell spray foam. Their typical thermal performance per inch ranges from roughly R-3.6 to R-7, with the higher numbers often associated with closed-cell foam and the lower with expanded polystyrene and mineral wool. However, real-world results depend on continuity. Gaps at edges, compressions at fasteners, and discontinuities at parapets can erode effective R-value by creating thermal bridges.
Professional assemblies treat those weak points head-on. Staggered, multiple insulation layers reduce linear heat paths; cover boards protect against foot traffic and hail; and compatible air or vapor control layers keep moisture from undermining performance. A smart detail is placing sufficient insulation above the deck to keep the dew point within the insulation layer during the coldest hours, lowering the risk of condensation on the interior side. Where interior humidity is high—think kitchens, pools, or manufacturing—vapor control becomes even more important to prevent moisture from diffusing into cool roof assemblies.
How much insulation is practical? The answer balances energy costs, climate, and structural limits. In heating-dominated zones, higher roof R-values deliver notable winter savings; in cooling-dominated zones, insulation pairs with reflective coatings to reduce peak load on mechanical systems. A helpful way to think about this is seasonal comfort:
– Winter: steady indoor temperatures, fewer cold spots near ceilings, gentler heating cycles.
– Summer: lower ceiling surface temperatures, slower heat flow after sunset, reduced reliance on peak cooling hours.
– All year: quieter interiors because insulation also dampens exterior noise on metal and membrane roofs.
Installation quality is where professional crews shine. They calibrate foam densities, verify board fastening patterns, and cut tight around penetrations to prevent air wash that degrades performance. They also coordinate with electricians and mechanical trades so later penetrations are properly sealed. When combined with a compatible coating system above, insulation becomes the thermos of the building envelope: it does not power the comfort, it preserves it, hour after hour, season after season.
Reflective Coatings: Cool Roof Science and Savings
Reflective coatings work by bouncing a large portion of solar energy away from the roof and by efficiently radiating absorbed heat back to the sky. Two numbers tell most of the story: solar reflectance (how much sunlight is reflected) and thermal emittance (how well a surface re-radiates heat). High-performing reflective roofs often start with solar reflectance above 0.70 and emittance around 0.80–0.90, producing a solar reflectance index that keeps rooftop temperatures far lower than dark surfaces. On a midsummer afternoon, that can mean surface temperatures 30–50°F lower than conventional colors, easing the workload on cooling equipment.
Lower roof temperatures create several knock-on benefits. Sealants, membranes, and insulation experience less thermal stress, which can mean fewer cracks and longer service intervals. Interiors feel more stable, especially in top-floor spaces or buildings with limited ductwork. Energy savings vary with climate, building type, and utility rates, but field studies frequently report double-digit reductions in cooling energy in hot regions and modest gains elsewhere. Even where summers are short, peak demand reduction during heat waves adds resilience when it matters most.
Performance over time depends on dirt pickup, biological growth, and weathering. Accumulated dust can reduce reflectance, sometimes by 0.05–0.15 over a few years, so light cleaning and drainage maintenance help preserve gains. Some reflective topcoats are more stain-resistant or better at shedding dirt in rainy climates, while others prioritize flexibility or ponding resistance. There is no single winner; selection should match climate and roof conditions. Useful questions to ask a professional include:
– What is the initial and aged reflectance-emittance profile for this system?
– How does the coating handle standing water?
– What cleaning schedule is realistic without specialized equipment?
Beyond energy, reflective roofs contribute to broader urban comfort by moderating local heat buildup around buildings. That neighborhood effect is hard to quantify for a single project, but when many surfaces swap deep color for high-reflectance finishes, evening temperatures can be gentler and air conditioning can cycle less. Pairing reflectivity with adequate insulation compounds benefits: the topcoat reduces heat input, and the insulation slows whatever remains. Think of it as a sunshield working with a thermal blanket, each making the other’s job easier.
Conclusion and Next Steps for Owners and Facility Managers
Choosing a coating strategy is ultimately a budgeting and risk decision. While prices vary by region and scope, ballpark figures help frame discussions: many liquid-applied coating systems land around $1.50–$5.00 per square foot depending on prep, reinforcement, and thickness; adding new rigid insulation can add $2.00–$5.00 per square foot per inch; a full tear-off and replacement often costs several times more. Savings emerge from deferred replacement, leak mitigation, and energy reductions. Simple payback for reflective and waterproofing upgrades can range from a few years in hot climates to longer spans in mild zones, with insulation payback tied tightly to heating and cooling hours. The most reliable wins come from stopping leaks and stabilizing indoor comfort, with energy savings as a valuable bonus.
A professional process turns those estimates into dependable outcomes. Look for crews that:
– Inspect and test: moisture scans, core samples, adhesion tests, and documented surface prep plans.
– Specify clearly: compatible primers, reinforcement at transitions, target wet and dry film thickness, and weather windows for each coat.
– Prove quality: in-progress photos, thickness readings, and a closeout report with maintenance notes.
– Plan service: a calendar for inspections—typically spring and fall—plus after major storms, and guidance on cleaning to preserve reflectance.
Maintenance keeps the return on track. Clear drains and scuppers, remove debris that traps moisture, and touch up damage at accessories before minor issues spread. Many systems are designed for recoat cycles in the 8–15 year range; planning for that future layer extends service life and avoids expensive surprises. Just as important, align the coating selection with roof use: high-traffic areas might need added protection; shaded zones might prioritize mildew resistance; ponding areas might call for higher ponding tolerance rather than maximum reflectivity.
For owners and facility managers weighing the next step, start with an assessment and a conversation grounded in building goals: leak risk, comfort targets, budget runway, and energy priorities. A tailored mix of waterproofing, insulation, and reflectivity can turn the roof from a vulnerability into a resilient asset. No single product can promise miracles, but a well-prepared surface, a compatible system, and a thoughtful maintenance plan will deliver steady, measurable value season after season.